
These electron configurations show that there are some similarities among each group of elements in terms of their valence electrons. Click on 'Element Atomic Number', 'Element Symbol', 'Element Name' and 'Element Valence Electrons' headers to sort. Valence electrons and families An electron configuration shows the number of electrons in each orbital in a particular atom. Here is a table representing the number of valence electrons of elements belonging to the second period and their electronic configuration.This Valence Electrons table gives the Valence Electrons of all the elements of periodic table. So, just by writing the electronic configuration of that element, we can quickly determine its number of valence electrons. The configuration of electrons gives a quick overview of the number of electrons present in the last shell. The arrangement of electrons in such orbitals is known as electronic configuration. The number of electrons in an atoms outermost valence shell governs its bonding behavior. Within the shells, electrons occupy a special place called atomic orbitals. By Using Electronic Configuration of the Element The table below depicts the number of valence electrons in the different groups of the periodic table: Periodic Table GroupĢ. A valence electron is an electron that is associated with an atom, and that can participate in the formation of a chemical bond in a single covalent bond, both atoms in the bond contribute one valence electron in order to form a shared pair. The rule applies to the transition and inner transition elements in groups 3-12. Point to Remember: Mostly for transition and inner transition elements, the valence electrons are the electrons present in the shells outside the noble gas core. This octet rule holds for elements in the second and third periods (or rows) of the periodic table. Thus the inner transition elements have valence electrons ranging from 3 to 16 (See above image of periodic table). However, this only holds for the main group elements, groups 1-2 and 13-18. This need to gain a filled valance electron shell by having 8 valence electrons is known as the octet rule and explains why certain elements are stable or unstable despite being electrically neutral. However, when mixed with O or H, the number of elements increases from 1-4 and then comes to 0. In contrast, the number of valence electrons across a period increases by one as we move left to right of a period.Įxception: As discussed, the period number indicates the number of shells, whereas the group number specifies the valence electron number in the outermost shell of an atom. Since filled d or f subshells are seldom disturbed in a chemical reaction, we can define valence electrons as follows: The electrons on an atom that are not. The valence periodic tables are availed in the oxidation state of elements with the help of the following grounds: While going from left to right in a valence periodic table, the number of electrons can change with an increment from 1-to 8. As we proceed downwards in a group, the numbers of valence electrons are same, although the number of shells increases. Here, we just refer to the periodic table and search for the position of the element in it. Group 1 elements have just one valence electron and group 18 elements have eight, except for helium, which has only two electrons total.
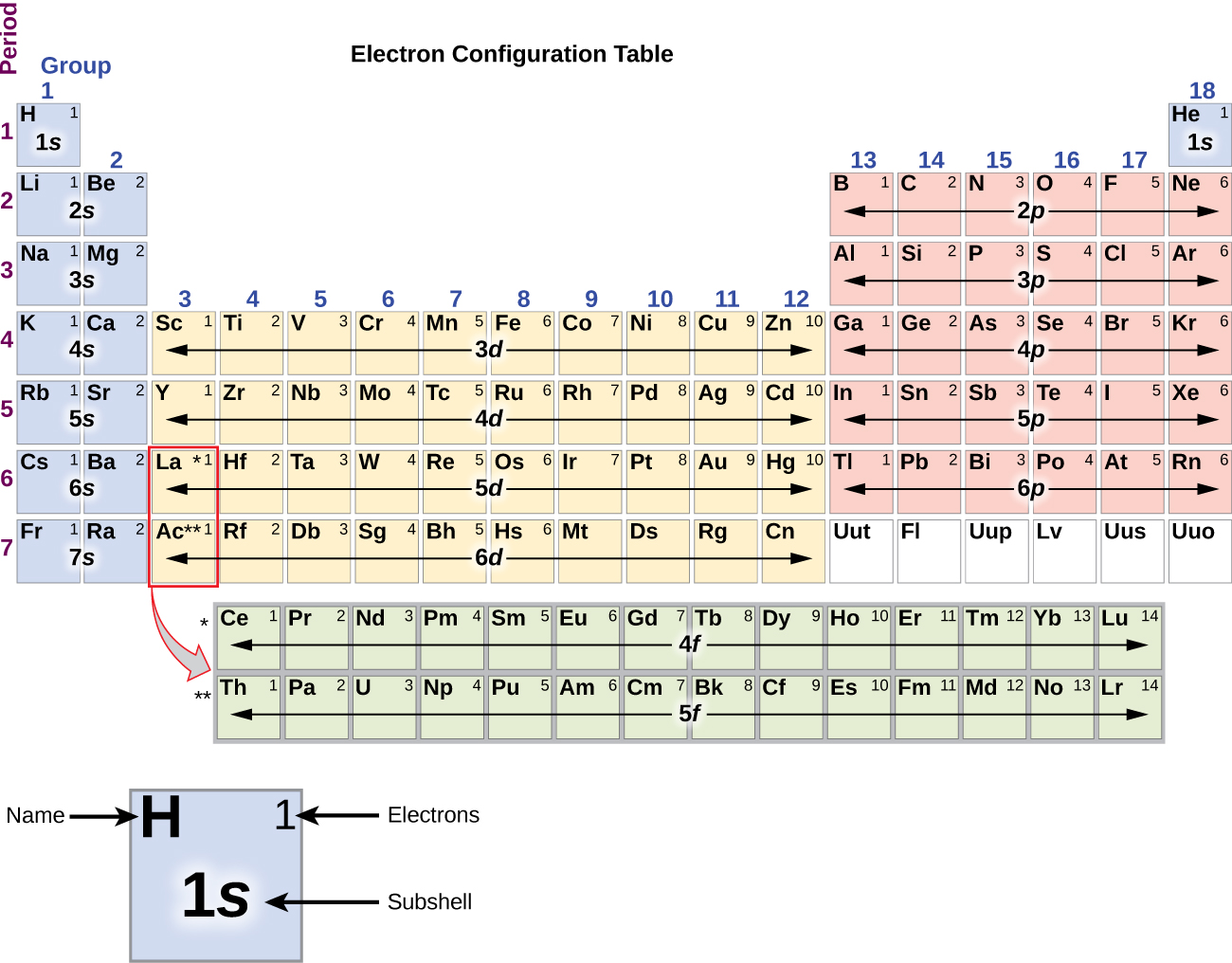
It is the most widely used method to determine the number of valence electrons in an element. There are two ways of calculating the number of valence electrons in an element.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
